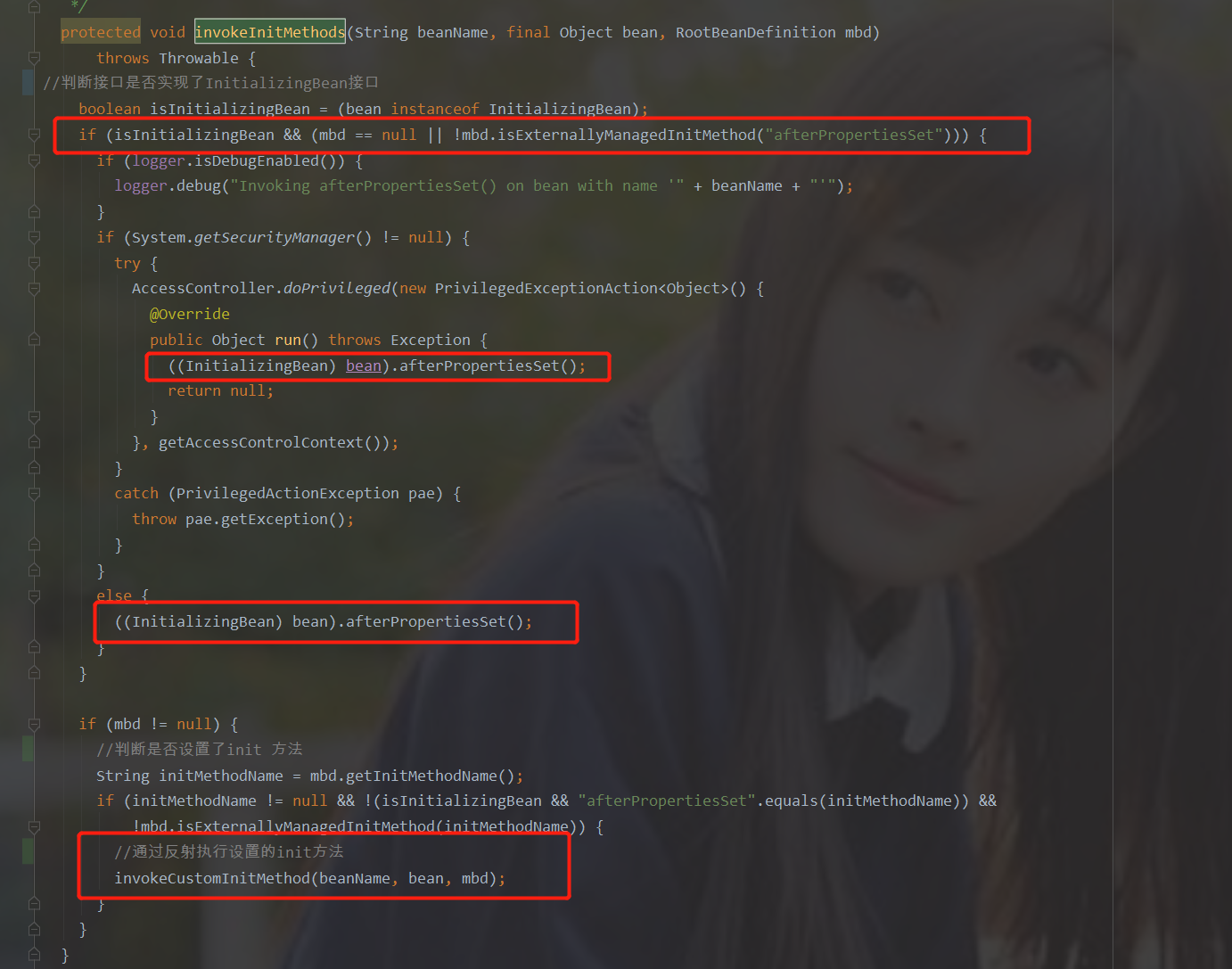
Java并发问题:死锁案例分析
死锁是Java并发编程中一个常见的问题。它发生在两个或更多进程互相等待对方释放资源的情况,此时所有进程都无法继续。
以下是一个经典的死锁案例:
// 进程A持有资源1,需要资源2class ProcessA implements Runnable {Resource1 r1;Resource2 r2;public ProcessA(Resource1 r1, Resource2 r2) {this.r1 = r1;this.r2 = r2;}@Overridepublic void run() {// 执行需要资源2的代码while (r2.isAvailable()) {// 释放资源1,等待资源2r1.release();try {// 等待资源2可用Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// 执行需要资源1的代码while (r1.isAvailable()) {r1.acquire();try {Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}// 进程B持有资源2,需要资源1class ProcessB implements Runnable {Resource2 r2;Resource1 r1;public ProcessB(Resource2 r2, Resource1 r1) {this.r2 = r2;this.r1 = r1;}@Overridepublic void run() {while (r1.isAvailable()) {r1.acquire();try {Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 执行需要资源2的代码,释放资源1r2.release();try {Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}while (r2.isAvailable()) {r2.acquire();try {Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}// 执行需要资源1的代码,释放资源2r1.release();try {Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}
在这个例子中,ProcessA持有Resource1和需要Resource2,而ProcessB持有Resource2和需要Resource1。
当两个进程都等待对方释放资源时(如ProcessA等待Resource2可用,ProcessB等待Resource1可用),就形成了死锁。






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...