k近邻算法matlab实现_k近邻算法
k 近邻法 (k-NN) 是一种基于实例的学习方法,无法转化为对参数空间的搜索问题(参数最优化 问题)。它的特点是对特征空间进行搜索。除了k近邻法,本章还对以下几个问题进行较深入的讨 论:
- 切比雪夫距离 的计算
- “近似误差” 与“估计误差” 的含义
- k-d树搜索算法图解
一、算法
输入:训练集 为实例特征向 为实例的类别,
输出:实例 所属的类
设在给定距离度量下,涵盖最近k个点的邻域为
其中示性函数 为真为假
寻找使得函数 取得最大值的变量 也就是说, 看看距离 最近的k个点里面哪一类别最多,以此作为输出。
二、模型
根据模型的分类, k-NN模型属于非概率模型。
观察 可发现它与感知机不同的之处, 作为决策函数, 它并不需要任何未知参数(感知机需要确定W和b),直接从训练集的数据得到输出。
1. 距离度量
k-NN的基本思想是,特征空间中的距离反映了两个点的相似程度, 因此 “距离” 是作出分类判断 的基本依据。向量空间 的距离有多种度量方式:
(1) 不同距离度量
一般形式是闵可夫斯基距离( 范数):
当p=1时, 称为曼哈顿距离( 范数):
当p=2时,称为欧几里得距离( 范数),也就是最常用的距离::
import mathfrom itertools import combinationsdef L(x, y, p=2):# x1 = [1, 1], x2 = [5,1]if len(x) == len(y) and len(x) > 1:sum = 0for i in range(len(x)):sum += math.pow(abs(x[i] - y[i]), p)return math.pow(sum, 1 / p)else:return 0
下图表示平面上A、B两点之间不同的距离:
- 只允许沿着坐标轴方向前进, 就像曼哈顿街区的出租车走过的距离
- 两点之间直线最短, 通过勾股定理计算斜边的距离
- 只剩下一个维度, 即最大的分量方向上的距离
可见p取值越大,两点之间的距离越短。
(2) 问题:为什么切比雪夫距离
其实这个问题等价于:为什么 即 空间中的向量 它的切比雪 夫长度等于它的最大分量方向上的长度。
证明: 设
不妨设 即
注意:最大分量的长度唯一, 但最大分量可能并不唯 一,设有x^{(1)}, x^{(2)}, \ldots x^{(k)}等个分量的长度都等于\left|x^{(1)}\right|$
当 即 为 时
当 即 为非最大长度分量时
计算 的切比雪夫长度:
由于已知 等于0或1,且有k个分量结果为1, 所以
因此
即 得证。
以上证明参考
(3) 平面上的圆
在平面上的图像: 如果圆形的定义是 “到某一点距离相等的曲线围成的图形” ,那么在不同的距离度量下,圆形的形 状可以完全不同。为何 正则化在平面上的等高线为同心正方形, 不就很容易理解吗?
如果圆形的定义是 “到某一点距离相等的曲线围成的图形” ,那么在不同的距离度量下,圆形的形 状可以完全不同。为何 正则化在平面上的等高线为同心正方形, 不就很容易理解吗?
- k值选择
李航老师书中引入了“近似误差”和“估计误差”两个概念,但没有给出具体定义。
这里简单总结一下:
右侧两项分别是 “估计误差” 和 “近似误差”
- 估计误差:训练集与无限数据集得到的模型的差距
近似误差:限制假设空间与无限制假设空间得到的模型的差距
- k值越小 单个样本影响越大 模型越复杂 假设空间越大 近似误差越小 (估计误差 越大),容易过拟合;
- k值越大 单个样本影响越小 模型越简单 假设空间越小 近似误差越大(估计误差 越小),容易欠拟合。
一般通过交叉验证来确定最优的 k 值。
- 决策规则
k 近邻的决策规则就是 “多数表决” ,即少数服从多数, 用数学表达式表示为
等号左侧为误分类率,要是误分类率最小,就要使得 最大, 即选择集合 中最多的一类。
三、kd树
kd 树的结构
kd树是一个二叉树结构,它的每一个节点记载了 [特征坐标, 切分轴, 指向左枝的指针, 指向右枝的指针] 。其中, 特征坐标是线性空间 中的一个点
切分轴由一个整数 表示, 这里 是我们在 维空间中沿第 维进行一次分割。节点的左枝和右枝分别都是 kd 树, 并且满足:如果 是左枝的一个特征坐标, 那么 并且如果 是右 枝的一个特征坐标,那么
给定一个数据样本集 和切分轴 以下递归算法将构建一个基于该数据集的 kd 树, 每一次循环制作一 个节点:
- 如果 记录 中唯一的一个点为当前节点的特征数据, 并且不设左枝和右枝。 指集合 中元素 . 的数量) 如果
如果
- 将 S 内所有点按照第 个坐标的大小进行排序;
- 选出该排列后的中位元素 (如果一共有偶数个元素, 则选择中位左边或右边的元素, 左或右并无影响),作为当前节点的特征坐标, 并且记录切分轴 将 设为在 中所有排列在中位元素之前的元素; 设为在 中所有排列在中位元素后的元素;
- 当前节点的左枝设为以 为数据集并且 为切分轴制作出的 树; 当前节点的右枝设为以 为数据集并且 为切分轴制作出 的 kd 树。再设 这里, 我们想轮流沿着每一个维度进 行分割; 是因为一共有 个维度, 在 沿着最后一个维度进行分割之后再重新回到第一个维度。)
构造 kd 树的例子
上面抽象的定义和算法确实是很不好理解,举一个例子会清楚很多。首先随机在 中随机生成 13 个点作为我们的数据集。起始的切分轴 这里 对应 轴, 而 对应 轴。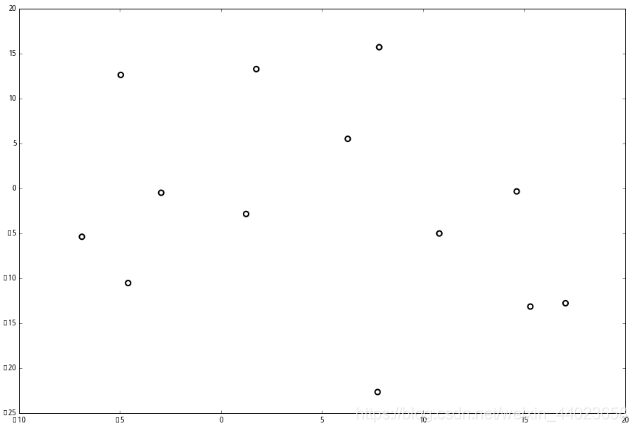 首先先沿 x 坐标进行切分,我们选出 x 坐标的中位点,获取最根部节点的坐标
首先先沿 x 坐标进行切分,我们选出 x 坐标的中位点,获取最根部节点的坐标
并且按照该点的x坐标将空间进行切分,所有 x 坐标小于 6.27 的数据用于构建左枝,x坐标大于 6.27 的点用于构建右枝。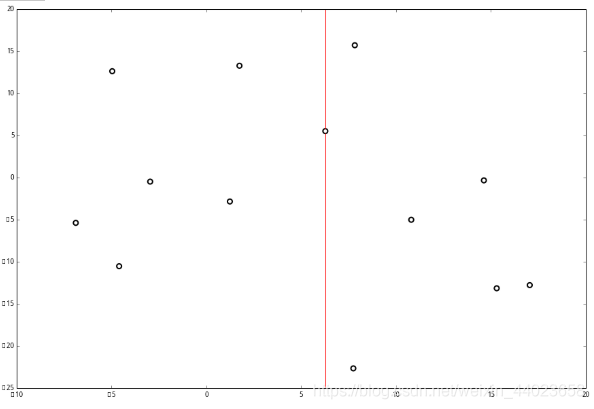 节点。得到下面的树,左边的x 是指这该层的节点都是沿 x 轴进行分割的。
节点。得到下面的树,左边的x 是指这该层的节点都是沿 x 轴进行分割的。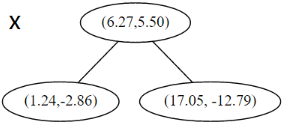 空间的切分如下
空间的切分如下 下一步中 对应 轴, 所以下面再按照 除标进行排序和切分,有
下一步中 对应 轴, 所以下面再按照 除标进行排序和切分,有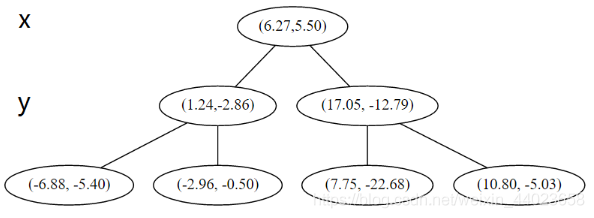
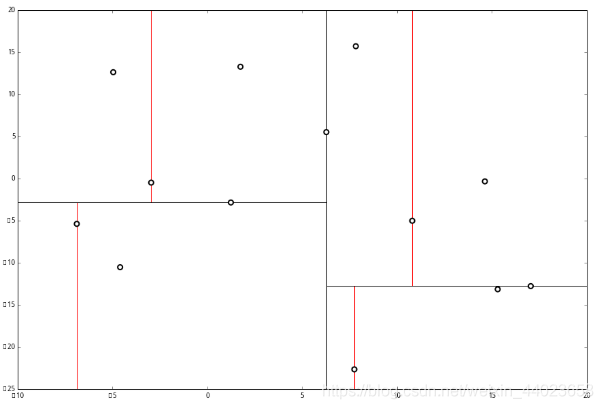 最后每一部分都只剩一个点,将他们记在最底部的节点中。因为不再有未被记录的点,所以不再进行切分。
最后每一部分都只剩一个点,将他们记在最底部的节点中。因为不再有未被记录的点,所以不再进行切分。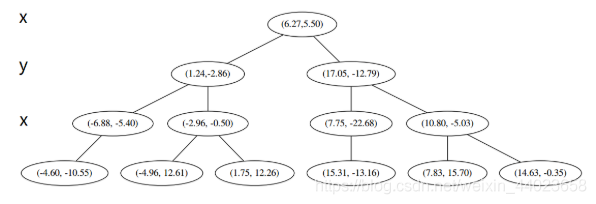
 就此完成了 kd 树的构造。
就此完成了 kd 树的构造。
kd 树上的 kNN 算法
给定一个构建于一个样本生的 kd 树, 下面的算法可以寻找距离某个点 最近的 个样本。
- 设 为一个有 个空位的列表, 用于保存已搜寻到的最近点.
- 根据 的坐标值和每个节点的切分向下搜素(也就是选,如果树的节点是按照 进行切分,并且 的 坐标小于 则向左枝进行搜索: 反之则走右枝)。
- 当达到一个底部节点时,将其标记为访问过. 如果 里不足 个点. 则将当前节点的特征坐标加人 如 果 L不为空并且当前节点 的特征与 的距离小于 里最长的距离,则用当前特征音换掉 中离 最远的点
如果当前节点不是整棵树最顶而节点, 执行 下(1):反之. 输出 算法完成. (1) . 向上爬一个节点。如果当前 (向上爬之后的) 节点未管被访问过, 将其标记为被访问过, 然后执行 1和2:如果当前节点被访 问过, 再次执行 (1)。
- 如果此时 里不足 个点, 则将节点特征加入 如果 中已满 个点, 且当前节点与 的距离小于 里最长的距离。则用节点特征豐换掉 中帝最远的点。
- 计算 和当前节点切分綫的距离。如果该距离大于等于 中距离 最远的距离井且 中已有 个点。则在切分线另一边不会有更近的点, 执行3: 如果该距离小于 中最远的距离或者 中不足 个点, 则切分綫另一边可能有更近的点, 因此在当前节点的另一个枝从 开始执行.
来看下面的例子: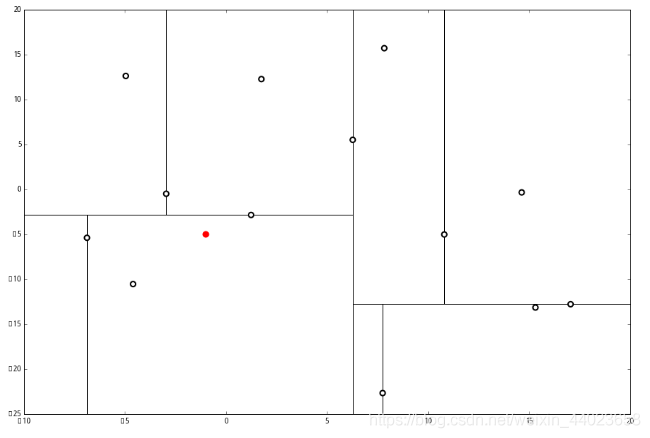 首先执行1,我们按照切分找到最底部节点。首先,我们在顶部开始
首先执行1,我们按照切分找到最底部节点。首先,我们在顶部开始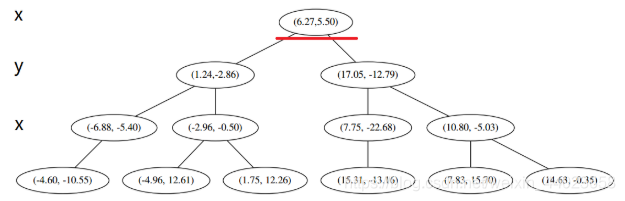 和这个节点的 x轴比较一下,
和这个节点的 x轴比较一下,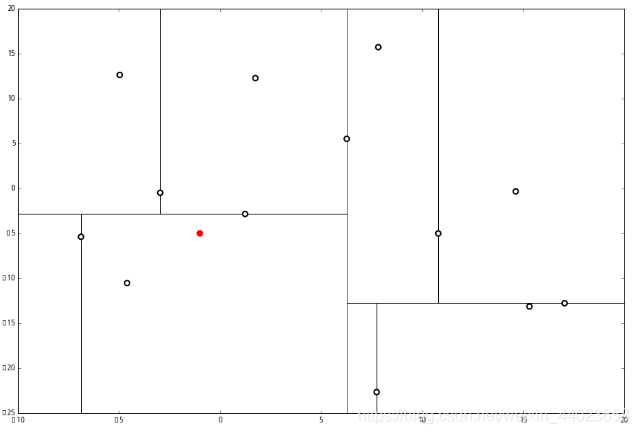 ppp 的 x 轴更小。因此我们向左枝进行搜索:
ppp 的 x 轴更小。因此我们向左枝进行搜索: 这次对比 y 轴,
这次对比 y 轴,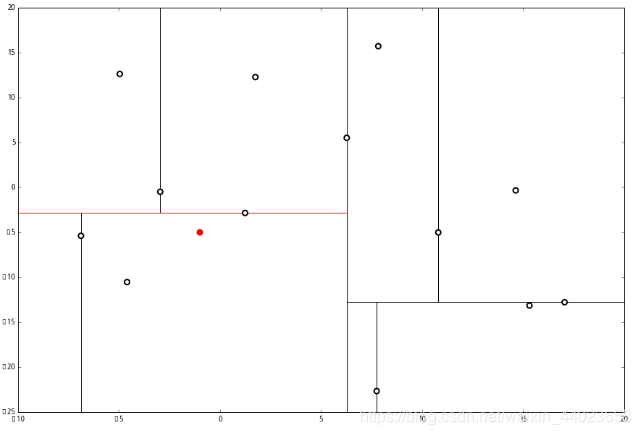 p 的 y 值更小,因此向左枝进行搜索:
p 的 y 值更小,因此向左枝进行搜索: 这个节点只有一个子枝,就不需要对比了。由此找到了最底部的节点 (−4.6,−10.55)。
这个节点只有一个子枝,就不需要对比了。由此找到了最底部的节点 (−4.6,−10.55)。 在二维图上是
在二维图上是 此时我们执行2。将当前结点标记为访问过, 并记录下 访问过的节点就在二叉树 上显示为被划掉的好了。
此时我们执行2。将当前结点标记为访问过, 并记录下 访问过的节点就在二叉树 上显示为被划掉的好了。
然后执行 3,不是最顶端节点。执行 (1),我爬。上面的是 (−6.88,−5.4)。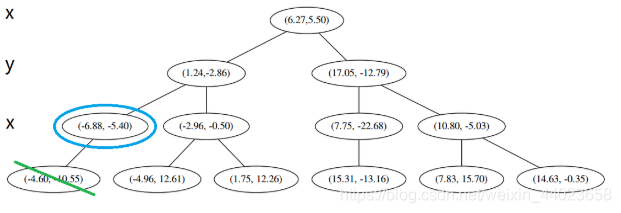
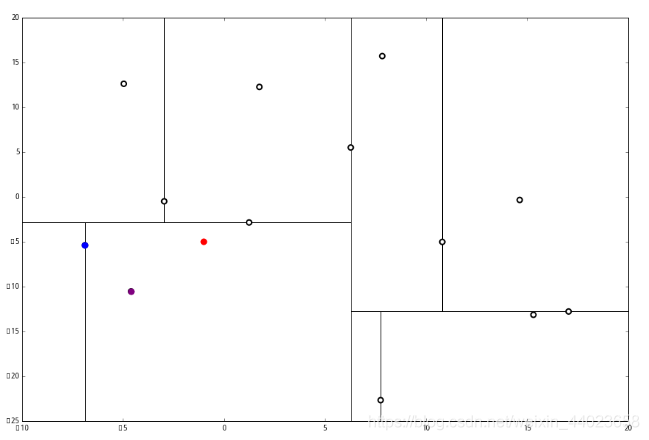
执行 1,因为我们记录下的点只有一个,小于k=3,所以也将当前节点记录下,有 L=[(−4.6,−10.55),(−6.88,−5.4)]。再执行 2,因为当前节点的左枝是空的,所以直接跳过,回到步骤3。3看了一眼,好,不是顶部,交给你了,(1)。于是乎 (1) 又往上爬了一节。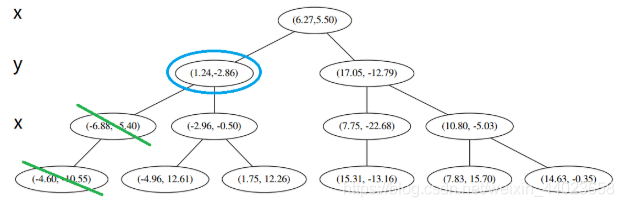
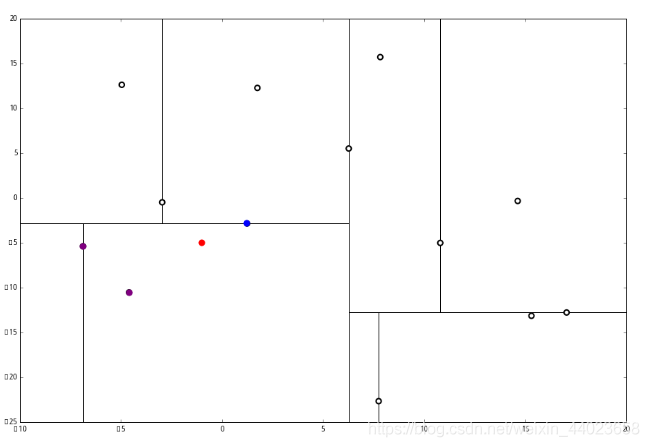 1 说,由于还是不够三个点,于是将当前点也记录下,有 L=[(−4.6,−10.55),(−6.88,−5.4),(1.24,−2.86)。当然,当前结点变为被访问过的。
1 说,由于还是不够三个点,于是将当前点也记录下,有 L=[(−4.6,−10.55),(−6.88,−5.4),(1.24,−2.86)。当然,当前结点变为被访问过的。
2又发现,当前节点有其他的分枝,并且经计算得出 p 点和 L 中的三个点的距离分别是 6.62,5.89,3.10,但是 p 和当前节点的分割线的距离只有 2.14,小于与 L 的最大距离: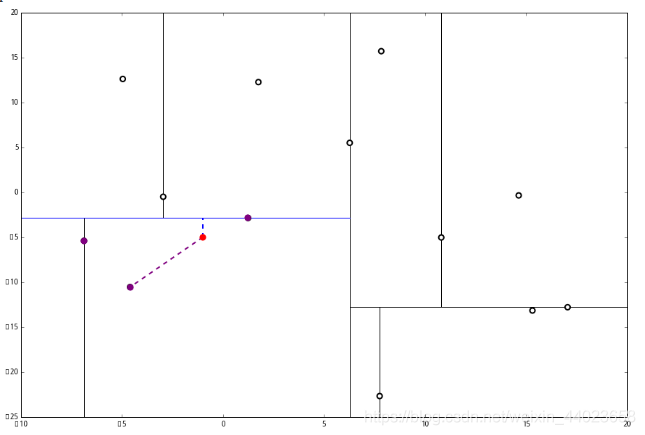 因此,在分割线的另一端可能有更近的点。于是我们在当前结点的另一个分枝从头执行 1。好,我们在红线这里:
因此,在分割线的另一端可能有更近的点。于是我们在当前结点的另一个分枝从头执行 1。好,我们在红线这里: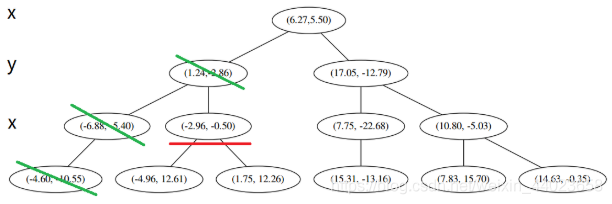 要用 p 和这个节点比较 x 坐标:
要用 p 和这个节点比较 x 坐标: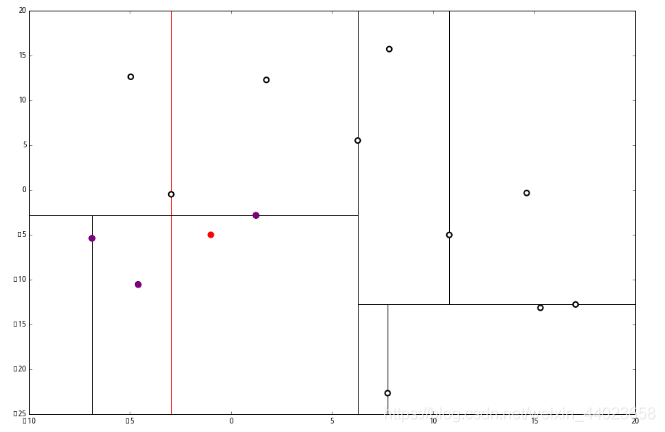 p 的x 坐标更大,因此探索右枝 (1.75,12.26),并且发现右枝已经是最底部节点,因此启动 2。
p 的x 坐标更大,因此探索右枝 (1.75,12.26),并且发现右枝已经是最底部节点,因此启动 2。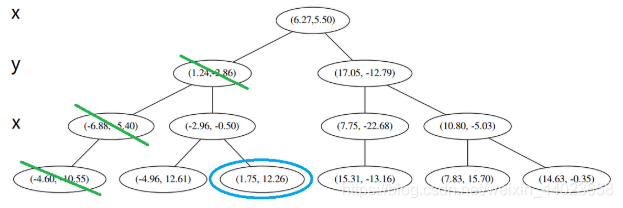 经计算,(1.75,12.26)与 p 的距离是 7.48,要大于 p 与 L 的距离,因此我们不将其放入记录中。
经计算,(1.75,12.26)与 p 的距离是 7.48,要大于 p 与 L 的距离,因此我们不将其放入记录中。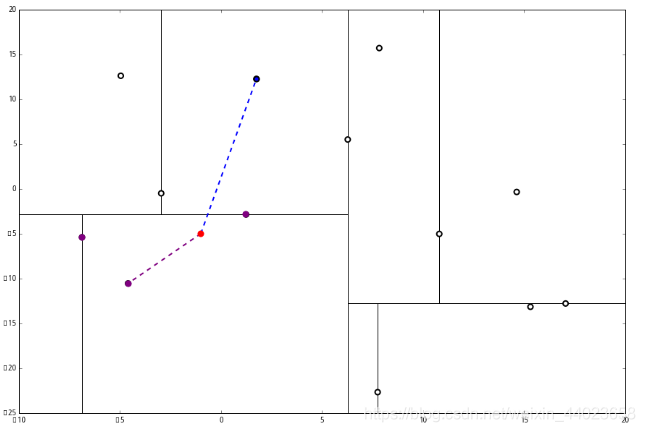 然后 3 判断出不是顶端节点,呼出 (1),爬。
然后 3 判断出不是顶端节点,呼出 (1),爬。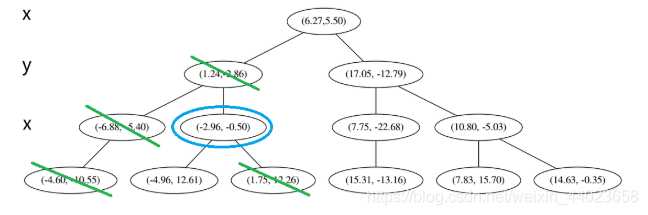 1出来一算,这个节点与 p 的距离是 4.91,要小于 p 与 L 的最大距离 6.62。
1出来一算,这个节点与 p 的距离是 4.91,要小于 p 与 L 的最大距离 6.62。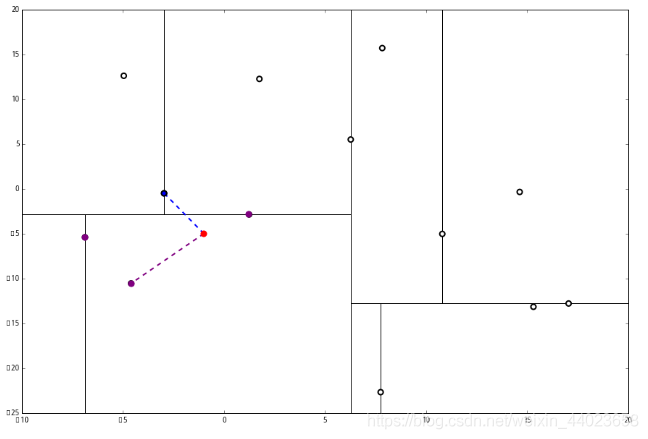 因此,我们用这个新的节点替代 L 中离 p 最远的 (−4.6,−10.55)。
因此,我们用这个新的节点替代 L 中离 p 最远的 (−4.6,−10.55)。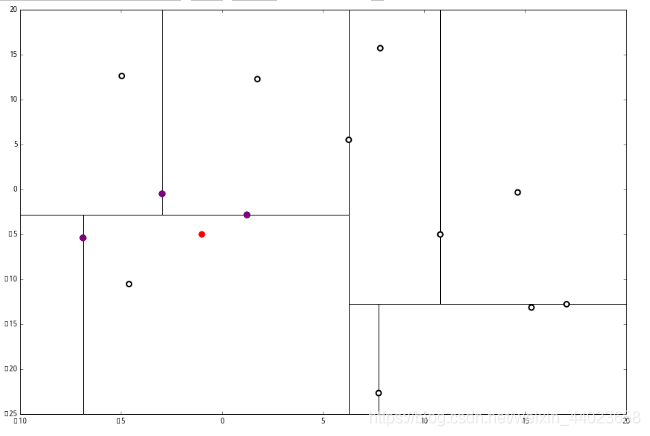 然后 2又来了,我们比对 p 和当前节点的分割线的距离
然后 2又来了,我们比对 p 和当前节点的分割线的距离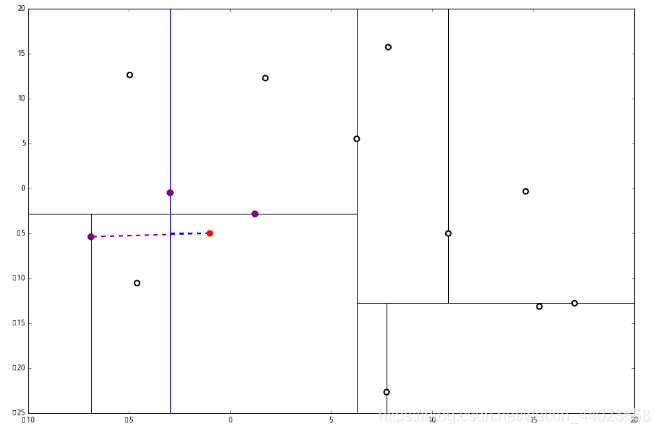 这个距离小于 L 与 p 的最小距离,因此我们要到当前节点的另一个枝执行 1。当然,那个枝只有一个点,直接到 2。
这个距离小于 L 与 p 的最小距离,因此我们要到当前节点的另一个枝执行 1。当然,那个枝只有一个点,直接到 2。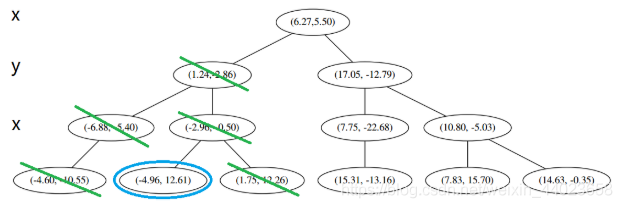 计算距离发现这个点离 p 比 L 更远,因此不进行替代。
计算距离发现这个点离 p 比 L 更远,因此不进行替代。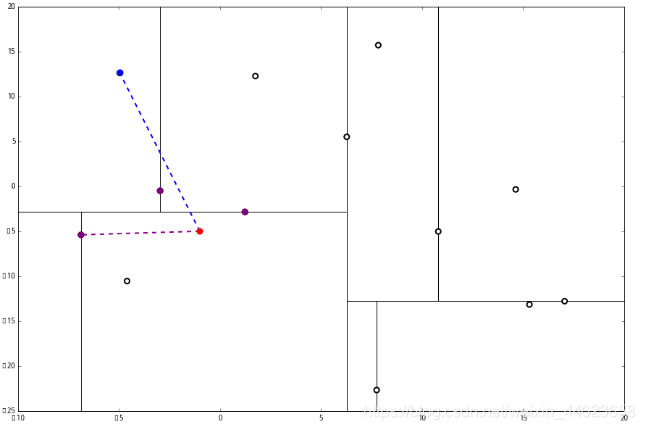 3发现不是顶点,所以呼出 (1)。我们向上爬,
3发现不是顶点,所以呼出 (1)。我们向上爬,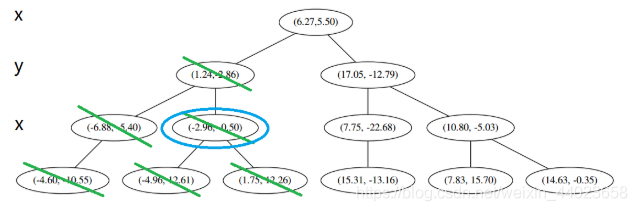 这个是已经访问过的了,所以再来(1),
这个是已经访问过的了,所以再来(1),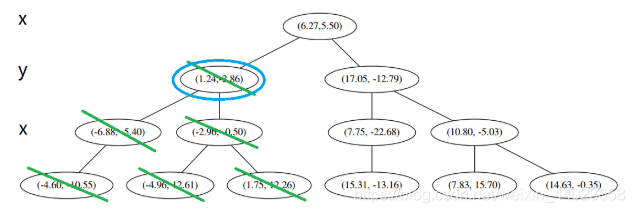 好,(1)再爬,
好,(1)再爬,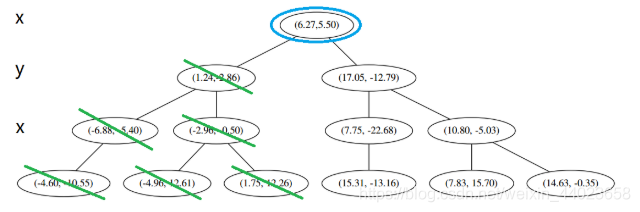 啊!到顶点了。所以完了吗?当然不,还没轮到 3 呢。现在是 1的回合。
啊!到顶点了。所以完了吗?当然不,还没轮到 3 呢。现在是 1的回合。
我们进行计算比对发现顶端节点与p的距离比L还要更远,因此不进行更新。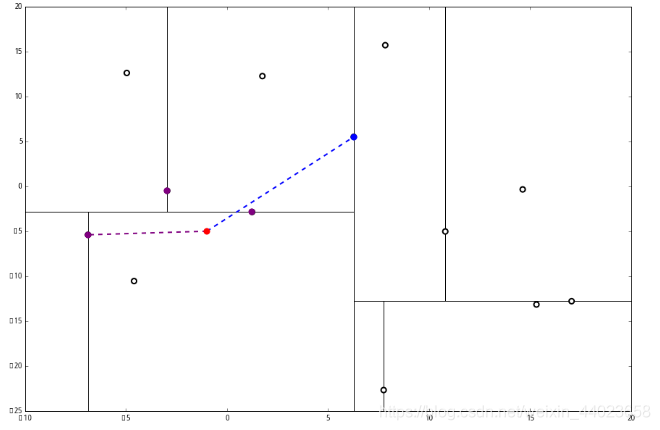 然后是 2,计算 p 和分割线的距离发现也是更远。
然后是 2,计算 p 和分割线的距离发现也是更远。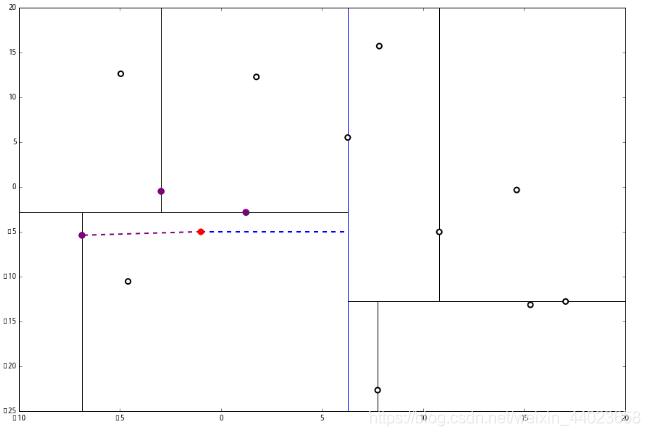 因此也不需要检查另一个分枝。
因此也不需要检查另一个分枝。
然后执行 3,判断当前节点是顶点,因此计算完成!输出距离 p 最近的三个样本是 L=[(−6.88,−5.4),(1.24,−2.86),(−2.96,−2.5)].
C实现
#include#include#include#include#include#include "kdtree.h"static inline int is_leaf(struct kdnode *node){return node->left == node->right;}static inline void swap(long *a, long *b){long tmp = *a;*a = *b;*b = tmp;}static inline double square(double d){return d * d;}static inline double distance(double *c1, double *c2, int dim){double distance = 0;while (dim-- > 0) {distance += square(*c1++ - *c2++);}return distance;}static inline double knn_max(struct kdtree *tree){return tree->knn_list_head.prev->distance;}static inline double D(struct kdtree *tree, long index, int r){return tree->coord_table[index][r];}static inline int kdnode_passed(struct kdtree *tree, struct kdnode *node){return node != NULL ? tree->coord_passed[node->coord_index] : 1;}static inline int knn_search_on(struct kdtree *tree, int k, double value, double target){return tree->knn_num }static inline void coord_index_reset(struct kdtree *tree){long i;for (i = 0; i capacity; i++) {tree->coord_indexes[i] = i;}}static inline void coord_table_reset(struct kdtree *tree){long i;for (i = 0; i capacity; i++) {tree->coord_table[i] = tree->coords + i * tree->dim;}}static inline void coord_deleted_reset(struct kdtree *tree){memset(tree->coord_deleted, 0, tree->capacity);}static inline void coord_passed_reset(struct kdtree *tree){memset(tree->coord_passed, 0, tree->capacity);}static void coord_dump_all(struct kdtree *tree){long i, j;for (i = 0; i count; i++) {long index = tree->coord_indexes[i];double *coord = tree->coord_table[index];printf("(");for (j = 0; j dim; j++) {if (j != tree->dim - 1) {printf("%.2f,", coord[j]);} else {printf("%.2f)\n", coord[j]);}}}}static void coord_dump_by_indexes(struct kdtree *tree, long low, long high, int r){long i;printf("r=%d:", r);for (i = 0; i <= high; i++) {if (i printf("%8s", " ");} else {long index = tree->coord_indexes[i];printf("%8.2f", tree->coord_table[index][r]);}}printf("\n");}static void bubble_sort(struct kdtree *tree, long low, long high, int r){long i, flag = high + 1;long *indexes = tree->coord_indexes;while (flag > 0) {long len = flag;flag = 0;for (i = low + 1; i if (D(tree, indexes[i], r) 1], r)) {swap(indexes + i - 1, indexes + i);flag = i;}}}}static void insert_sort(struct kdtree *tree, long low, long high, int r){long i, j;long *indexes = tree->coord_indexes;for (i = low + 1; i <= high; i++) {long tmp_idx = indexes[i];double tmp_value = D(tree, indexes[i], r);j = i - 1;for (; j >= low && D(tree, indexes[j], r) > tmp_value; j--) {indexes[j + 1] = indexes[j];}indexes[j + 1] = tmp_idx;}}static void quicksort(struct kdtree *tree, long low, long high, int r){if (high - low <= 32) {insert_sort(tree, low, high, r);//bubble_sort(tree, low, high, r);return;}long *indexes = tree->coord_indexes;/* median of 3 */long mid = low + (high - low) / 2;if (D(tree, indexes[low], r) > D(tree, indexes[mid], r)) {swap(indexes + low, indexes + mid);}if (D(tree, indexes[low], r) > D(tree, indexes[high], r)) {swap(indexes + low, indexes + high);}if (D(tree, indexes[high], r) > D(tree, indexes[mid], r)) {swap(indexes + high, indexes + mid);}/* D(indexes[low]) <= D(indexes[high]) <= D(indexes[mid]) */double pivot = D(tree, indexes[high], r);/* 3-way partition* +---------+-----------+---------+-------------+---------+* | pivot | <=pivot | ? | >=pivot | pivot |* +---------+-----------+---------+-------------+---------+* low lt i j gt high*/long i = low - 1;long lt = i;long j = high;long gt = j;for (; ;) {while (D(tree, indexes[++i], r) while (D(tree, indexes[--j], r) > pivot && j > low) {}if (i >= j) break;swap(indexes + i, indexes + j);if (D(tree, indexes[i], r) == pivot) swap(&indexes[++lt], &indexes[i]);if (D(tree, indexes[j], r) == pivot) swap(&indexes[--gt], &indexes[j]);}/* i == j or j + 1 == i */swap(indexes + i, indexes + high);/* Move equal elements to the middle of array */long x, y;for (x = low, j = i - 1; x <= lt && j > lt; x++, j--) swap(indexes + x, indexes + j);for (y = high, i = i + 1; y >= gt && iquicksort(tree, low, j - lt + x - 1, r);quicksort(tree, i + y - gt, high, r);}static struct kdnode *kdnode_alloc(double *coord, long index, int r){struct kdnode *node = malloc(sizeof(*node));if (node != NULL) {memset(node, 0, sizeof(*node));node->coord = coord;node->coord_index = index;node->r = r;}return node;}static void kdnode_free(struct kdnode *node){free(node);}static int coord_cmp(double *c1, double *c2, int dim){int i;double ret;for (i = 0; i ret = *c1++ - *c2++;if (fabs(ret) >= DBL_EPSILON) {return ret > 0 ? 1 : -1;}}if (fabs(ret) return 0;} else {return ret > 0 ? 1 : -1;}}static void knn_list_add(struct kdtree *tree, struct kdnode *node, double distance){if (node == NULL) return;struct knn_list *head = &tree->knn_list_head;struct knn_list *p = head->prev;if (tree->knn_num == 1) {if (p->distance > distance) {p = p->prev;}} else {while (p != head && p->distance > distance) {p = p->prev;}}if (p == head || coord_cmp(p->node->coord, node->coord, tree->dim)) {struct knn_list *log = malloc(sizeof(*log));if (log != NULL) {log->node = node;log->distance = distance;log->prev = p;log->next = p->next;p->next->prev = log;p->next = log;tree->knn_num++;}}}static void knn_list_adjust(struct kdtree *tree, struct kdnode *node, double distance){if (node == NULL) return;struct knn_list *head = &tree->knn_list_head;struct knn_list *p = head->prev;if (tree->knn_num == 1) {if (p->distance > distance) {p = p->prev;}} else {while (p != head && p->distance > distance) {p = p->prev;}}if (p == head || coord_cmp(p->node->coord, node->coord, tree->dim)) {struct knn_list *log = head->prev;/* Replace the original max one */log->node = node;log->distance = distance;/* Remove from the max position */head->prev = log->prev;log->prev->next = head;/* insert as a new one */log->prev = p;log->next = p->next;p->next->prev = log;p->next = log;}}static void knn_list_clear(struct kdtree *tree){struct knn_list *head = &tree->knn_list_head;struct knn_list *p = head->next;while (p != head) {struct knn_list *prev = p;p = p->next;free(prev);}tree->knn_num = 0;}static void resize(struct kdtree *tree){tree->capacity *= 2;tree->coords = realloc(tree->coords, tree->dim * sizeof(double) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_table = realloc(tree->coord_table, sizeof(double *) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_indexes = realloc(tree->coord_indexes, sizeof(long) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_deleted = realloc(tree->coord_deleted, sizeof(char) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_passed = realloc(tree->coord_passed, sizeof(char) * tree->capacity);coord_table_reset(tree);coord_index_reset(tree);coord_deleted_reset(tree);coord_passed_reset(tree);}static void kdnode_dump(struct kdnode *node, int dim){int i;if (node->coord != NULL) {printf("(");for (i = 0; i if (i != dim - 1) {printf("%.2f,", node->coord[i]);} else {printf("%.2f)\n", node->coord[i]);}}} else {printf("(none)\n");}}void kdtree_insert(struct kdtree *tree, double *coord){if (tree->count + 1 > tree->capacity) {resize(tree);}memcpy(tree->coord_table[tree->count++], coord, tree->dim * sizeof(double));}static void knn_pickup(struct kdtree *tree, struct kdnode *node, double *target, int k){double dist = distance(node->coord, target, tree->dim);if (tree->knn_num knn_list_add(tree, node, dist);} else {if (dist knn_list_adjust(tree, node, dist);} else if (fabs(dist - knn_max(tree)) knn_list_add(tree, node, dist);}}}static void kdtree_search_recursive(struct kdtree *tree, struct kdnode *node, double *target, int k, int *pickup){if (node == NULL || kdnode_passed(tree, node)) {return;}int r = node->r;if (!knn_search_on(tree, k, node->coord[r], target[r])) {return;}if (*pickup) {tree->coord_passed[node->coord_index] = 1;knn_pickup(tree, node, target, k);kdtree_search_recursive(tree, node->left, target, k, pickup);kdtree_search_recursive(tree, node->right, target, k, pickup);} else {if (is_leaf(node)) {*pickup = 1;} else {if (target[r] <= node->coord[r]) {kdtree_search_recursive(tree, node->left, target, k, pickup);kdtree_search_recursive(tree, node->right, target, k, pickup);} else {kdtree_search_recursive(tree, node->right, target, k, pickup);kdtree_search_recursive(tree, node->left, target, k, pickup);}}/* back track and pick up */if (*pickup) {tree->coord_passed[node->coord_index] = 1;knn_pickup(tree, node, target, k);}}}void kdtree_knn_search(struct kdtree *tree, double *target, int k){if (k > 0) {int pickup = 0;kdtree_search_recursive(tree, tree->root, target, k, &pickup);}}void kdtree_delete(struct kdtree *tree, double *coord){int r = 0;struct kdnode *node = tree->root;struct kdnode *parent = node;while (node != NULL) {if (node->coord == NULL) {if (parent->right->coord == NULL) {break;} else {node = parent->right;continue;}}if (coord[r] coord[r]) {parent = node;node = node->left;} else if (coord[r] > node->coord[r]) {parent = node;node = node->right;} else {int ret = coord_cmp(coord, node->coord, tree->dim);if (ret 0) {parent = node;node = node->left;} else if (ret > 0) {parent = node;node = node->right;} else {node->coord = NULL;break;}}r = (r + 1) % tree->dim;}}static void kdnode_build(struct kdtree *tree, struct kdnode **nptr, int r, long low, long high){if (low == high) {long index = tree->coord_indexes[low];*nptr = kdnode_alloc(tree->coord_table[index], index, r);} else if (low /* Sort and fetch the median to build a balanced BST */quicksort(tree, low, high, r);long median = low + (high - low) / 2;long median_index = tree->coord_indexes[median];struct kdnode *node = *nptr = kdnode_alloc(tree->coord_table[median_index], median_index, r);r = (r + 1) % tree->dim;kdnode_build(tree, &node->left, r, low, median - 1);kdnode_build(tree, &node->right, r, median + 1, high);}}static void kdtree_build(struct kdtree *tree){kdnode_build(tree, &tree->root, 0, 0, tree->count - 1);}void kdtree_rebuild(struct kdtree *tree){long i, j;size_t size_of_coord = tree->dim * sizeof(double);for (i = 0, j = 0; j count; i++, j++) {while (j count && tree->coord_deleted[j]) {j++;}if (i != j && j count) {memcpy(tree->coord_table[i], tree->coord_table[j], size_of_coord);tree->coord_deleted[i] = 0;}}tree->count = i;coord_index_reset(tree);kdtree_build(tree);}struct kdtree *kdtree_init(int dim){struct kdtree *tree = malloc(sizeof(*tree));if (tree != NULL) {tree->root = NULL;tree->dim = dim;tree->count = 0;tree->capacity = 65536;tree->knn_list_head.next = &tree->knn_list_head;tree->knn_list_head.prev = &tree->knn_list_head;tree->knn_list_head.node = NULL;tree->knn_list_head.distance = 0;tree->knn_num = 0;tree->coords = malloc(dim * sizeof(double) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_table = malloc(sizeof(double *) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_indexes = malloc(sizeof(long) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_deleted = malloc(sizeof(char) * tree->capacity);tree->coord_passed = malloc(sizeof(char) * tree->capacity);coord_index_reset(tree);coord_table_reset(tree);coord_deleted_reset(tree);coord_passed_reset(tree);}return tree;}static void kdnode_destroy(struct kdnode *node){if (node == NULL) return;kdnode_destroy(node->left);kdnode_destroy(node->right);kdnode_free(node);}void kdtree_destroy(struct kdtree *tree){kdnode_destroy(tree->root);knn_list_clear(tree);free(tree->coords);free(tree->coord_table);free(tree->coord_indexes);free(tree->coord_deleted);free(tree->coord_passed);free(tree);}#define _KDTREE_DEBUG#ifdef _KDTREE_DEBUGstruct kdnode_backlog {struct kdnode *node;int next_sub_idx;};void kdtree_dump(struct kdtree *tree){int level = 0;struct kdnode *node = tree->root;struct kdnode_backlog nbl, *p_nbl = NULL;struct kdnode_backlog nbl_stack[KDTREE_MAX_LEVEL];struct kdnode_backlog *top = nbl_stack;for (; ;) {if (node != NULL) {/* Fetch the pop-up backlogged node's sub-id.* If not backlogged, fetch the first sub-id. */int sub_idx = p_nbl != NULL ? p_nbl->next_sub_idx : KDTREE_RIGHT_INDEX;/* Backlog should be left in next loop */p_nbl = NULL;/* Backlog the node */if (is_leaf(node) || sub_idx == KDTREE_LEFT_INDEX) {top->node = NULL;top->next_sub_idx = KDTREE_RIGHT_INDEX;} else {top->node = node;top->next_sub_idx = KDTREE_LEFT_INDEX;}top++;level++;/* Draw lines as long as sub_idx is the first one */if (sub_idx == KDTREE_RIGHT_INDEX) {int i;for (i = 1; i if (i == level - 1) {printf("%-8s", "+-------");} else {if (nbl_stack[i - 1].node != NULL) {printf("%-8s", "|");} else {printf("%-8s", " ");}}}kdnode_dump(node, tree->dim);}/* Move down according to sub_idx */node = sub_idx == KDTREE_LEFT_INDEX ? node->left : node->right;} else {p_nbl = top == nbl_stack ? NULL : --top;if (p_nbl == NULL) {/* End of traversal */break;}node = p_nbl->node;level--;}}}#endif
python
class kdtree(object):# 创建 kdtree# point_list 是一个 list 的 pair,pair[0] 是一 tuple 的特征,pair[1] 是类别def __init__(self, point_list, depth=0, root=None):if len(point_list)>0:# 轮换按照树深度选择坐标轴k = len(point_list[0][0])axis = depth % k# 选中位线,切point_list.sort(key=lambda x:x[0][axis])median = len(point_list) // 2self.axis = axisself.root = rootself.size = len(point_list)# 造节点self.node = point_list[median]# 递归造左枝和右枝if len(point_list[:median])>0:self.left = kdtree(point_list[:median], depth+1, self)else:self.left = Noneif len(point_list[median+1:])>0:self.right = kdtree(point_list[median+1:], depth+1, self)else:self.right = None# 记录是按哪个方向切的还有树根else:return None# 在树上加一点def insert(self, point):self.size += 1# 分析是左还是右,递归加在叶子上if point[0][self.axis]0][self.axis]:if self.left!=None:self.left.insert(point)else:self.left = kdtree([point], self.axis+1, self)else:if self.right!=None:self.right.insert(point)else:self.right = kdtree([point], self.axis+1, self)# 输入一点# 按切分寻找叶子def find_leaf(self, point):if self.left==None and self.right==None:return selfelif self.left==None:return self.right.find_leaf(point)elif self.right==None:return self.left.find_leaf(point)elif point[self.axis]0][self.axis]:return self.left.find_leaf(point)else:return self.right.find_leaf(point)# 查找最近的 k 个点,复杂度 O(DlogN),D是维度,N是树的大小# 输入一点、一距离函数、一k。距离函数默认是 L_2def knearest(self, point, k=1, dist=lambda x,y: sum(map(lambda u,v:(u-v)**2,x,y))):# 往下戳到最底叶leaf = self.find_leaf(point)# 从叶子网上爬return leaf.k_down_up(point, k, dist, result=[], stop=self, visited=None)# 从下往上爬函数,stop是到哪里去,visited是从哪里来def k_down_up(self, point,k, dist, result=[],stop=None, visited=None):# 选最长距离if result==[]:max_dist = 0else:max_dist = max([x[1] for x in result])other_result=[]# 如果离分界线的距离小于现有最大距离,或者数据点不够,就从另一边的树根开始刨if (self.left==visited and self.node[0][self.axis]-point[self.axis]and self.right!=None)\or (len(result)and self.left==visited and self.right!=None):other_result=self.right.knearest(point,k, dist)if (self.right==visited and point[self.axis]-self.node[0][self.axis]and self.left!=None)\or (len(result)and self.right==visited and self.left!=None):other_result=self.left.knearest(point, k, dist)# 刨出来的点放一起,选前 k 个result.append((self.node, dist(point, self.node[0])))result = sorted(result+other_result, key=lambda pair: pair[1])[:k]# 到停点就返回结果if self==stop:return result# 没有就带着现有结果接着往上爬else:return self.root.k_down_up(point,k, dist, result, stop, self)# 输入 特征、类别、k、距离函数# 返回这个点属于该类别的概率def kNN_prob(self, point, label, k, dist=lambda x,y: sum(map(lambda u,v:(u-v)**2,x,y))):nearests = self.knearest(point, k, dist)return float(len([pair for pair in nearests if pair[0][1]==label]))/float(len(nearests))# 输入 特征、k、距离函数# 返回该点概率最大的类别以及相对应的概率def kNN(self, point, k, dist=lambda x,y: sum(map(lambda u,v:(u-v)**2,x,y))):nearests = self.knearest(point, k , dist)statistics = {}for data in nearests:label = data[0][1]if label not in statistics:statistics[label] = 1else:statistics[label] += 1max_label = max(statistics.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1))[0]return max_label, float(statistics[max_label])/float(len(nearests))






























还没有评论,来说两句吧...