python数据类型之‘字典‘
1.为什么需要字典类型
**>>> list1 = [“name”, “age”, “gender”]
list2 = [“fentiao”, 5, “male”]
zip(list1, list2)**>>>userinfo=dict(zip(list1, list2))
//通过zip内置函数将两个列表结合
[(‘name’, ‘fentiao’), (‘age’, 5), (‘gender’, ‘male’)]
list2[0]
//在直接编程时,并不能理解第一个索引表示姓名
‘fentiao’
list2[name]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File ““, line 1, in
TypeError: list indices must be integers, not str
故字典是python中唯一的映射类型,key-value(哈希表),字典对象是可变的,但key必须用不可变对象。
2.字典的定义
1.定义一个空字典
s = {}
print(type(s))
d = dict()print(d, type(d))
2.定义含元素的字典
s = {'fentiao':[100, 80, 90],'westos':[100,100,100]}print(s, type(s))d = dict(a=1, b=2)print(d, type(d))

字典的key-value值,称为键值对
其中key值必须为不可变对象。
value值可以是任意数据类型: int,float,long, complex, list, tuple,set, dict
3.内建方法:fromkeys
字典中的key有相同的value值,默认为None
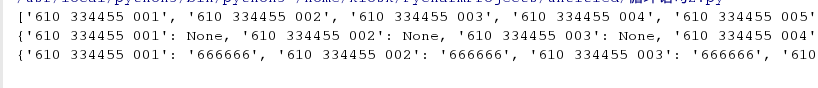
例:随机生成100张卡号, 卡号的格式为610 334455 001 —-610 334455 100,且初始密码均为666666
cards = []
for cardId in range(100):
card = “610 334455 %.3d” %(cardId+1)
cards.append(card)
print(cards)print({}.fromkeys(cards))
print({}.fromkeys(cards, ‘666666’))
4.字典的嵌套
students = {
‘13021001’: {
‘name’:’张龙’,
‘age’:18,
‘score’:100
},
‘13021003’: {
‘name’: ‘张’,
‘age’: 18,
‘score’: 90
}
}
print(students[‘13021003’][‘name’])

2.字典的特性
由于字典无序,所以不支持索引,切片,重复,连接,只支持成员操作符
1..成员操作符, 默认判断key值是否存在.
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
print(‘a’ in d)
print(1 in d)

2. for循环: 默认遍历字典的key值;
for i in d:
print(i)
3.枚举
for i,v in enumerate(d):
print(i, ‘——-‘, v)
#
3.字典的常用方法
1、取出字典中对应的值(两种方法)
1).根据key取出字典中的值,(注意: key不存在, 就会报错)
d = dict(a=1, b=2)a = d['a']print(a)
2).get( )函数,获取字典中对应key的值,如果key不存在,取默认值None,如果需要指定返回的值, 传值即可
如果key存在,取出对应的结果
d = dict(a=1, b=2)print(d.get('a'))print(d.get('c'))

2.查看keys与values
services = {'http':80,'mysql':3306}# 查看字典里面所有的key值print(services.keys())# 查看字典里面所有的value值print(services.values())# 查看字典里面所有的key-value值print(services.items())# 遍历
for k,v in services.items():
print(k , ‘—->’, v)for k in services:
print(k, ‘—->’, services[k])


3.key-value的增加
1.dict[key] = value
#添加或者更改key-value对
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
d[‘g’] = 10
d[‘a’] = 10
print(d)
2 dict.upate{}
#如果key值已经存在, 更新value值;
#如果key值不存在, 添加key-value值;
d = dict(a=1, b=2)
d.update({‘a’:4, ‘f’:1})
print(d)
3.dict.setdefault()
# 如果key值已经存在, 不做修改;
# 如果key值不存在, 添加key-value值;默认情况下value值为Noned = dict(a=1, b=2)
d.setdefault(‘g’, 10)()
print(d)
4.字典的删除
1.根据key值删除字典的元素
dic.pop(key)
del dic[‘key’]
2.随机删除字典元素,返回(key,value)
dic.popitem()
3.删除字典中的所有元素
dic.clear()
4.删除字典本身
del dic
4.练习
1.输入一段话,求某个单词出现的次数,以字典的方式输出
1)
words=input("请输入一句话:")li=words.split(' ')print(li)#word=dict{li}word = ({}.fromkeys(li))for word1 in word:#word = ({}.fromkeys(li))if word1 in word:word[word1]=1else:word[word1]+=1print(word)

2)
from collections import Counterfrom collections import defaultdicts=input('s:')li=s.split()wordDict = defaultdict(int)for word in li:wordDict[word]+=1print(wordDict.items())c=Counter(wordDict)print(c.most_common())

2.列表去重
#1. 转换为集合
li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 65, 1, 2, 3]
print(list(set(li)))#2.字典的方式
li=[1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1]
print({}.fromkeys(li).keys())
3.间接实现switch语句
while True: grade=input("请输入你的等级:") d={ 'A':"优秀", 'B':"良好", 'C':"合格" } print(d.get(grade,"成绩无效"))


































还没有评论,来说两句吧...