使用最新的 hbase-client 2.1 操作 hbase
文章目录
- 概述
- 直接使用hbase-client
- 引入依赖
- 配置文件
- 编写测试代码
概述
springboot 2.1 集成 hbase2.1
环境说明:
hbase:2.1.5
springboot:2.1.1.RELEASE
hadoop :2.8.5
java: 8+
hadoop环境:Hadoop 2.8.5 完全分布式HA高可用安装(二)–环境搭建
hbase环境:hbase 2.1 环境搭建–完全分布式模式 Advanced - Fully Distributed
直接使用hbase-client
引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId><artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId><version>2.1.5</version></dependency>
配置文件
将 hbase-site.xml和core-site.xml两个文件拷贝到resource文件夹下: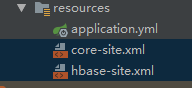
由于上述两个文件中配置了虚拟机中名称,所以要在maven工程所在的机器中配置hosts,我的是Windows,修改C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc中的hosts文件:
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.# 127.0.0.1 localhost# ::1 localhost192.168.229.128 node1192.168.229.129 node2192.168.229.130 node3192.168.229.131 node4
编写测试代码
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.*;import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.compress.Compression;import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;import java.io.IOException;import java.net.URISyntaxException;public class HelloHBase {public static void main(String[] args) throws URISyntaxException {// 加载HBase的配置Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();// 读取配置文件configuration.addResource(new Path(ClassLoader.getSystemResource("hbase-site.xml").toURI()));configuration.addResource(new Path(ClassLoader.getSystemResource("core-site.xml").toURI()));try (// 创建一个HBase连接Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(configuration);// 获得执行操作的管理接口Admin admin = connection.getAdmin();) {// 新建一个表名为mytable的表TableName tableName = TableName.valueOf("mytable");HTableDescriptor tableDescriptor = new HTableDescriptor(tableName);// 新建一个列族名为mycf的列族HColumnDescriptor mycf = new HColumnDescriptor("mycf");// 将列族添加到表中tableDescriptor.addFamily(mycf);// 执行建表操作createOrOverwrite(admin, tableDescriptor);// 设置列族的压缩方式为GZmycf.setCompactionCompressionType(Compression.Algorithm.GZ);// 设置最大版本数量(ALL_VERSIONS实际上就是Integer.MAX_VALUE)mycf.setMaxVersions(HConstants.ALL_VERSIONS);// 列族更新到表中tableDescriptor.modifyFamily(mycf);// 执行更新操作admin.modifyTable(tableName, tableDescriptor);// 新增一个列族HColumnDescriptor hColumnDescriptor = new HColumnDescriptor("newcf");hColumnDescriptor.setCompactionCompressionType(Compression.Algorithm.GZ);hColumnDescriptor.setMaxVersions(HConstants.ALL_VERSIONS);// 执行新增操作admin.addColumnFamily(tableName, hColumnDescriptor);// 获取表对象Table table = connection.getTable(tableName);// 创建一个put请求,用于添加数据或者更新数据Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("jack"));table.put(put);// 创建一个append请求,用于在数据后面添加内容Append append = new Append(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));append.add(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("son"));table.append(append);// 创建一个long类型的列Put put1 = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("row2"));put1.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes(6L));table.put(put1);// 创建一个增值请求,将值增加10LIncrement increment = new Increment(Bytes.toBytes("row2"));increment.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), 10L);table.increment(increment);// 创建一个查询请求,查询一行数据Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));// 由于HBase的一行可能非常大,所以限定要取出的列族get.addFamily(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"));// 创建一个结果请求Result result = table.get(get);// 从查询结果中取出name列,然后打印(这里默认取最新版本的值,如果要取其他版本要使用Cell对象)byte[] name = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"), Bytes.toBytes("name"));System.out.println(Bytes.toString(name));// 创建一个查询请求,查询一行数据get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("row2"));// 由于HBase的一行可能非常大,所以限定要取出的列族get.addFamily(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"));// 创建一个结果请求result = table.get(get);// 从查询结果中取出name列,然后打印(这里默认取最新版本的值,如果要取其他版本要使用Cell对象)byte[] age = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"), Bytes.toBytes("age"));System.out.println(Bytes.toLong(age));//注意格式// 创建一个扫描请求,查询多行数据Scan scan = new Scan(Bytes.toBytes("row1"));// 设置扫描器的缓存数量,遍历数据时不用发多次请求,默认100,适当的缓存可以提高性能scan.setCaching(150);// 创建扫描结果,这个时候不会真正从HBase查询数据,下面的遍历才是去查询ResultScanner resultScanner = table.getScanner(scan);for (Result r : resultScanner) {String data = Bytes.toString(r.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"), Bytes.toBytes("name")));System.out.println(data);}// 使用完毕关闭resultScanner.close();// 创建一个删除请求Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes("row2"));// 可以自定义一些筛选条件delete.addFamily(Bytes.toBytes("mycf"));table.delete(delete);// 停用表admin.disableTable(tableName);// 删除列族admin.deleteColumnFamily(tableName, "mycf".getBytes());// 删除表admin.deleteTable(tableName);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("ok");}public static void createOrOverwrite(Admin admin, HTableDescriptor table) throws IOException {// 获取table名TableName tableName = table.getTableName();// 判断table是否存在,如果存在则先停用并删除if (admin.tableExists(tableName)) {// 停用表admin.disableTable(tableName);// 删除表admin.deleteTable(tableName);}// 创建表admin.createTable(table);}}
上面展示了一个完整的创建,插入,查询,删除的过程。读者可以debug并配合hbase shell 来查看数据变化。































还没有评论,来说两句吧...